What is the Kalman Filter?
TLDR:
The Kalman Filter is an optimal estimation algorithm that predicts the future states of a system based on its previous states, especially useful for data with noise, offering estimates close to real values.
Overview
The Kalman Filter, while termed as a “filter,” is actually an algorithm that predicts the future states of a system by considering its prior states. Estimating future states based on past data is relatively straightforward, but the unique strength of the Kalman Filter lies in its ability to work with noisy (uncertain) data, producing estimates that approach reality as closely as possible.
History of the Kalman Filter
Developed by mathematician Rudolf Kalman, the Kalman Filter is among the 20th century’s most notable inventions and was integral to the Apollo space program. In the Apollo program, the team needed to estimate the internal temperature of the spacecraft’s main engine, which reached extreme temperatures up to 5500°F. Direct measurement wasn’t feasible, so the Kalman Filter was used to estimate the internal temperature based on external readings. This solution was essential due to multiple influencing factors, such as varying fuel flow rates and atmospheric conditions, which impacted the readings with noise.
How the Kalman Filter Works
The Kalman Filter predicts a system’s future states by constructing a mathematical model of the system.
— What is a Mathematical Model?
A mathematical model functions as a formula or function, taking input parameters and returning output values. While linear systems are relatively easy to model, non-linear systems can be challenging. Creating a model that accurately mirrors the real system is important since real-world data is often noisy and imprecise, and unexpected factors may affect the system’s behavior.
— Operational Principle
By utilizing the closest possible model, the Kalman Filter predicts the state of the system using input and output data from the model.
Applications and Purpose of the Kalman Filter
The Kalman Filter is ideal for dynamic systems where information is uncertain or incomplete. It helps infer the actual state of a system based on its inputs and outputs, making it suitable for cases where direct measurements are unreliable or noisy. The filter aids in obtaining the most accurate estimation when sensor data contains noise, making it valuable in real-world applications.
Kalman Filter State Observation
State Observation enables the estimation of data that is not directly measurable.
Mathematical Model and State Observation
Creating a mathematical model that closely resembles the actual system enables similar behavior in the model. For instance, in estimating the temperature of a rocket motor in space, a direct sensor measurement isn’t feasible due to extreme heat. Therefore, an external sensor is used, providing indirect data. The Kalman Filter then enables temperature estimation, aiding in decisions such as fuel flow and speed adjustments.
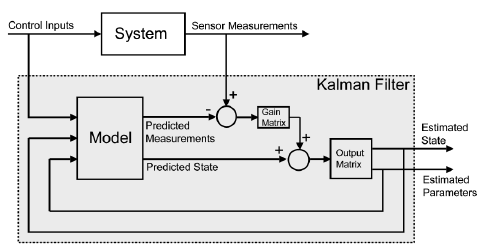
Fuel flow serves as the system’s input, while the sensor reading provides observational data. By aligning the inputs of the model with those of the real system, minimal discrepancy between the model’s output and sensor readings indicates high accuracy. When the model’s outputs align with sensor data, the Kalman Filter facilitates the estimation of internal system states, allowing predictions about internal temperatures.
Kalman Filter Python Library — Filterpy
The Filterpy library provides implementations of Kalman and Bayesian filters in Python. Using the kalman module, the filter class can be applied without delving into further details.
pip install filterpy
filterpy.__version__ # Version test and information.