Arduino Sample Projects
Settings for Arduino IDE:
- In the
Toolsmenu:- Board: Arduino Uno
- Port: dev/ttyUSB0
- Programmer: AVRISP mkll
Contents
- Arduino Sample Projects
- Contents
- LED Lighting Guide
- Sending Information to Serial Monitor When Button is Pressed
- Buzzer Activated by Button Press
- LED Activated by Button Press
- Turning on a Lamp with a Single Relay
- Turning on Lamps with a Dual Relay
- Lightning Effect with 5 LEDs
- 16x02 LCD Usage: “Hello World” Example
- Displaying Two Button States on the LCD Screen
- Writing MPU6050 Data to the Serial Monitor
- Writing Rotary Switch Data to the Serial Monitor
LED Lighting Guide
Wiring Diagram
- The long leg of the LED is the anode (+), and the short leg is the cathode (-).
- Connect a 220Ω resistor to the anode (+) leg.
- The other end of the resistor connects to one of the digital pins on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 7).
- Connect the cathode (-) leg to the Arduino’s GND (ground [-]) pin.
Wiring Instructions:
- GND –> LED (-)
- LED (+) –> 220Ω Resistor –> Pin 7
Sample Code
#define LED_PIN 7 // The digital pin the LED is connected to
void setup() {
// Set LED_PIN as an output
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the LED on
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Turn the LED off
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Explanation
- LED_PIN: Defines the digital pin to which the LED is connected. In this example, the LED is connected to Pin 7.
- setup(): Sets LED_PIN as an output.
- loop(): The LED lights up for 1 second, then turns off for 1 second. This cycle repeats continuously.
With this simple circuit and code, you can easily control an LED with an Arduino.
Sending Information to Serial Monitor When Button is Pressed
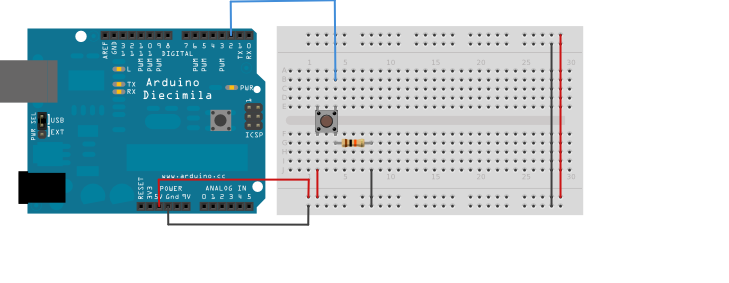
Wiring Diagram
- Connect one end of the button to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 2).
- The other end connects to the GND (ground [-]) pin.
- Additionally, connect the button’s Arduino end to the 5V pin via a 10kΩ resistor.
Wiring Instructions:
- Button –> Pin 2
- Button –> GND
- Button –> 10kΩ Resistor –> 5V
Note 1: The GND and resistor should connect to the same side of the button.
Note 2: The pin connection should be on the opposite side of the button.
Sample Code
#define BUTTON_PIN 2 // The digital pin the button is connected to
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == HIGH) {
Serial.println("Button Pressed!");
delay(500); // Short delay to prevent multiple presses
}
}
Explanation
- BUTTON_PIN: The digital pin to which the button is connected. In this example, the button is connected to Pin 2.
- setup(): Serial communication is started, and BUTTON_PIN is set as an input.
- loop(): When the button is pressed, the message “Button Pressed!” is sent to the serial monitor.
Buzzer Activated by Button Press
Wiring Diagram
- Connect one end of the button to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 2).
- The other end connects to the GND (ground [-]) pin.
- Additionally, connect the button’s Arduino end to the 5V pin via a 10kΩ resistor.
- Connect the positive (+) lead of the buzzer to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 8), and the negative (-) lead to the GND pin.
Wiring Instructions:
- Button –> Pin 2
- Button –> GND
- Button –> 10kΩ Resistor –> 5V
- Buzzer (+) –> Pin 8
- Buzzer (-) –> GND
Note 1: The GND and resistor should connect to the same side of the button.
Note 2: The pin connection should be on the opposite side of the button.
Sample Code
#define BUTTON_PIN 2 // The digital pin the button is connected to
#define BUZZER_PIN 8 // The digital pin the buzzer is connected to
void setup() {
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(BUZZER_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(BUZZER_PIN, HIGH); // Activate the buzzer
} else {
digitalWrite(BUZZER_PIN, LOW); // Deactivate the buzzer
}
}
Explanation
- BUTTON_PIN: The digital pin to which the button is connected.
- BUZZER_PIN: The digital pin to which the buzzer is connected.
- setup(): BUTTON_PIN is set as an input, and BUZZER_PIN is set as an output.
- loop(): The buzzer is activated when the button is pressed and deactivated when released.
LED Activated by Button Press
Wiring Diagram
- Connect one end of the button to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 2).
- The other end connects to the GND (ground [-]) pin.
- Additionally, connect the button’s Arduino end to the 5V pin via a 10kΩ resistor.
- Connect the anode (+) of the LED to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 7) via a 220Ω resistor. Connect the cathode (-) to the GND pin.
Wiring Instructions:
- Button –> Pin 2
- Button –> GND
- Button –> 10kΩ Resistor –> 5V
- LED (+) –> 220Ω Resistor –> Pin 7
- LED (-) –> GND
Sample Code
#define BUTTON_PIN 2 // The digital pin the button is connected to
#define LED_PIN 7 // The digital pin the LED is connected to
void setup() {
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
} else {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); // Turn off the LED
}
}
Explanation
- BUTTON_PIN: The digital pin to which the button is connected.
- LED_PIN: The digital pin to which the LED is connected.
- setup(): BUTTON_PIN is set as an input, and LED_PIN is set as an output.
- loop(): The LED turns on when the button is pressed and turns off when released.
Turning on a Lamp with a Single Relay
Wiring Diagram
- Connect the control pin of the relay to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 4).
- Connect the lamp to the NO (Normally Open) and COM pins of the relay.
- The lamp connects to a power source.
Wiring Instructions:
- Relay IN –> Pin 4
- Lamp –> Relay NO and COM pins
- Lamp –> Power source
Sample Code
#define RELAY_PIN 4 // The digital pin the relay is connected to
void setup() {
pinMode(RELAY_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, HIGH); // Turn on the lamp
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, LOW); // Turn off the lamp
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Explanation
- RELAY_PIN: The digital pin to which the relay is connected.
- setup(): RELAY_PIN is set as an output.
- loop(): The lamp turns on for 1 second, then turns off for 1 second.
Turning on Lamps with a Dual Relay
Wiring Diagram
- Connect the control pin of the first relay to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 4).
- Connect the control pin of the second relay to another digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 5).
- Connect the lamps to the NO (Normally Open) and COM pins of the relays.
- The lamps connect to a power source.
Wiring Instructions:
- 1st Relay IN –> Pin 4
- 2nd Relay IN –> Pin 5
- Lamps –> Relay NO and COM pins
- Lamps –> Power source
Sample Code
#define RELAY1_PIN 4 // The digital pin the 1st relay is connected to
#define RELAY2_PIN 5 // The digital pin the 2nd relay is connected to
void setup() {
pinMode(RELAY1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RELAY2_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(RELAY1_PIN, HIGH); // Turn on the 1st lamp
digitalWrite(RELAY2_PIN, HIGH); // Turn on the 2nd lamp
delay(1000); // Wait for
1 second
digitalWrite(RELAY1_PIN, LOW); // Turn off the 1st lamp
digitalWrite(RELAY2_PIN, LOW); // Turn off the 2nd lamp
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Explanation
- RELAY1_PIN: The digital pin to which the 1st relay is connected.
- RELAY2_PIN: The digital pin to which the 2nd relay is connected.
- setup(): RELAY1_PIN and RELAY2_PIN are set as outputs.
- loop(): The lamps turn on for 1 second, then turn off for 1 second.
: Sets LED_PIN as output.
- loop(): Adjusts LED brightness based on the potentiometer value.
Lightning Effect with 5 LEDs
Circuit Diagram
- The anode (+) of each LED is connected to one of the digital pins (e.g., Pin 2, Pin 3, Pin 4, Pin 5, Pin 6) via a 220Ω resistor.
- The cathode (-) of the LEDs is connected to GND.
Connection Instructions:
- LED1 (+) –> 220Ω Resistor –> Pin 2
- LED2 (+) –> 220Ω Resistor –> Pin 3
- LED3 (+) –> 220Ω Resistor –> Pin 4
- LED4 (+) –> 220Ω Resistor –> Pin 5
- LED5 (+) –> 220Ω Resistor –> Pin 6
- LED (-) –> GND
Sample Code
#define LED1_PIN 2
#define LED2_PIN 3
#define LED3_PIN 4
#define LED4_PIN 5
#define LED5_PIN 6
void setup() {
pinMode(LED1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED2_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED3_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED4_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED5_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Lightning effect
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
digitalWrite(LED1_PIN, HIGH);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED1_PIN, LOW);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED2_PIN, HIGH);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED2_PIN, LOW);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED3_PIN, HIGH);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED3_PIN, LOW);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED4_PIN, HIGH);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED4_PIN, LOW);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED5_PIN, HIGH);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED5_PIN, LOW);
delay(100);
}
}
Explanation
- LED1_PIN, LED2_PIN, LED3_PIN, LED4_PIN, LED5_PIN: The digital pins connected to the LEDs.
- setup(): Sets LED pins as outputs.
- loop(): LEDs turn on and off sequentially, creating a lightning effect.
Here’s the translated text:
16x02 LCD Usage: “Hello World” Example
Connection Diagram
- The LCD’s VCC pin is connected to the 5V pin.
- The LCD’s GND pin is connected to the GND pin.
- The LCD’s VO pin is connected to GND through a potentiometer (10kΩ) for contrast adjustment.
- The LCD’s RS pin is connected to a digital pin (e.g., Pin 12) on the Arduino.
- The LCD’s RW pin is connected to GND.
- The LCD’s E pin is connected to a digital pin (e.g., Pin 11) on the Arduino.
- The LCD’s D0-D3 pins are not used.
- The LCD’s D4-D7 pins are connected to digital pins (e.g., Pin 5, 4, 3, 2).
Connection Instructions:
- LCD VCC –> 5V
- LCD GND –> GND
- LCD VO –> Potentiometer –> GND
- LCD RS –> Pin 12
- LCD RW –> GND
- LCD E –> Pin 11
- LCD D4 –> Pin 5
- LCD D5 –> Pin 4
- LCD D6 –> Pin 3
- LCD D7 –> Pin 2
Example Code
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> // Include the LCD library
// Define LCD pins
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);
void setup() {
lcd.begin(16, 2); // Initialize the LCD with 16 columns and 2 rows
lcd.print("Hello, World!"); // Print "Hello, World!" to the LCD
}
void loop() {
// Code can continue here
}
Explanation
- LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);: Defines the LCD pins.
- lcd.begin(16, 2);: Sets the number of rows and columns for the LCD.
- lcd.print(“Hello, World!”);: Displays “Hello, World!” on the LCD.
This basic example allows you to display messages on your LCD screen.
Displaying Two Button States on the LCD Screen
Connection Diagram
- The LCD connection is the same as in the previous example.
- Both buttons are connected to digital pins:
- Button 1: one end is connected to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 2), and the other end is connected to the GND pin.
- Button 2: one end is connected to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 3), and the other end is connected to the GND pin.
- Also, a pull-down resistor (10kΩ) is connected to GND for each button.
Connection Instructions:
- Button 1 –> Pin 2
- Button 1 –> GND
-
Button 1 –> 10kΩ Resistor –> 5V
- Button 2 –> Pin 3
- Button 2 –> GND
- Button 2 –> 10kΩ Resistor –> 5V
Example Code
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> // Include the LCD library
// Define LCD pins
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);
// Define button pins
#define BUTTON1_PIN 2
#define BUTTON2_PIN 3
void setup() {
lcd.begin(16, 2); // Initialize the LCD with 16 columns and 2 rows
pinMode(BUTTON1_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP); // Set button pins as input with pull-up resistor
pinMode(BUTTON2_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
void loop() {
int button1State = digitalRead(BUTTON1_PIN); // Read the state of Button 1
int button2State = digitalRead(BUTTON2_PIN); // Read the state of Button 2
lcd.clear(); // Clear the LCD screen
lcd.setCursor(0, 0); // Move to the first row
lcd.print("Button 1: ");
lcd.print(button1State == LOW ? "Pressed" : "Released"); // Display the state of Button 1
lcd.setCursor(0, 1); // Move to the second row
lcd.print("Button 2: ");
lcd.print(button2State == LOW ? "Pressed" : "Released"); // Display the state of Button 2
delay(500); // Wait for 0.5 seconds
}
Explanation
- LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);: Defines the LCD pins.
- pinMode(BUTTON1_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);: Sets button pins as input with a pull-up resistor.
- digitalRead(BUTTON1_PIN);: Reads the state of Button 1.
- lcd.print(button1State == LOW ? “Pressed” : “Released”);: Displays “Pressed” or “Released” based on Button 1’s state.
- lcd.clear();: Clears the LCD screen on each loop.
This example shows the states of two buttons on the LCD screen. When the buttons are pressed, “Pressed” will be displayed; when not pressed, “Released” will be shown.
Writing MPU6050 Data to the Serial Monitor
Connection Diagram
- The MPU6050’s VCC pin is connected to the 5V pin.
- The MPU6050’s GND pin is connected to the GND pin.
- The MPU6050’s SDA pin is connected to Arduino’s A4 pin (or I2C SDA pin).
- The MPU6050’s SCL pin is connected to Arduino’s A5 pin (or I2C SCL pin).
Connection Instructions:
- MPU6050 VCC –> 5V
- MPU6050 GND –> GND
- MPU6050 SDA –> A4 (or I2C SDA)
- MPU6050 SCL –> A5 (or I2C SCL)
Example Code
The following code reads data from the MPU6050 sensor and writes this data to the serial monitor. You will need the Wire and MPU6050 libraries. You can download the MPU6050 library here.
#include <Wire.h> // Include the I2C library
#include <MPU6050.h> // Include the MPU6050 library
MPU6050 mpu; // Create an MPU6050 object
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication
Wire.begin(); // Start I2C communication
mpu.initialize(); // Initialize the MPU6050
if (!mpu.testConnection()) {
Serial.println("MPU6050 connection failed!");
while (1); // Infinite loop if connection fails
}
}
void loop() {
int16_t ax, ay, az;
int16_t gx, gy, gz;
mpu.getAcceleration(&ax, &ay, &az); // Read accelerometer data
mpu.getRotation(&gx, &gy, &gz); // Read gyroscope data
Serial.print("Acceleration: X=");
Serial.print(ax);
Serial.print(" Y=");
Serial.print(ay);
Serial.print(" Z=");
Serial.println(az);
Serial.print("Gyroscope: X=");
Serial.print(gx);
Serial.print(" Y=");
Serial.print(gy);
Serial.print(" Z=");
Serial.println(gz);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Explanation
- Wire.h: Required for I2C communication.
- MPU6050.h: Required for MPU6050 sensor.
- mpu.initialize();: Initializes the MPU6050 sensor.
- mpu.getAcceleration(&ax, &ay, &az);: Reads accelerometer data.
- mpu.getRotation(&gx, &gy, &gz);: Reads gyroscope data.
- Serial.print() and Serial.println(): Writes data to the serial monitor.
This code reads acceleration and gyroscope data from the MPU6050 sensor and prints it to the serial monitor every second.
Writing Rotary Switch Data to the Serial Monitor
Connection Diagram
A rotary switch typically has 3 or 4 pins and is connected as follows:
- Common Pin: Connected to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 2).
- CLK (Clock) Pin: Connected to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 3).
- DT (Data) Pin: Connected to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 4).
- SW (Switch) Pin (if present): Connected to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., Pin 5).
Connection Instructions:
- Rotary Common –> Pin 2
- Rotary CLK –> Pin 3
- Rotary DT –> Pin 4
- Rotary SW (if present) –> Pin 5
- Rotary GND –> GND
Example Code
The following code reads the direction of a rotary switch and whether the button
is pressed, and writes this information to the serial monitor. This example is for a rotary encoder and button combination.
#define ENCODER_CLK_PIN 3 // CLK pin connected to this digital pin
#define ENCODER_DT_PIN 4 // DT pin connected to this digital pin
#define BUTTON_PIN 5 // SW pin connected to this digital pin (if present)
volatile int encoderPos = 0; // Encoder position
int lastEncoderPos = 0; // Last read encoder position
bool buttonPressed = false; // Button state
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication
pinMode(ENCODER_CLK_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(ENCODER_DT_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(ENCODER_CLK_PIN), handleEncoder, CHANGE);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(BUTTON_PIN), handleButton, FALLING);
}
void loop() {
if (encoderPos != lastEncoderPos) {
if (encoderPos > lastEncoderPos) {
Serial.println("Turned right");
} else {
Serial.println("Turned left");
}
lastEncoderPos = encoderPos;
}
if (buttonPressed) {
Serial.println("Pressed");
buttonPressed = false;
}
delay(100); // Wait for 0.1 seconds
}
void handleEncoder() {
int dtState = digitalRead(ENCODER_DT_PIN);
if (dtState == HIGH) {
encoderPos++;
} else {
encoderPos--;
}
}
void handleButton() {
buttonPressed = true;
}
Explanation
- ENCODER_CLK_PIN: Digital pin connected to the rotary encoder’s CLK pin.
- ENCODER_DT_PIN: Digital pin connected to the rotary encoder’s DT pin.
- BUTTON_PIN: Digital pin connected to the rotary encoder’s button (if present).
- handleEncoder(): Reads rotary encoder movement and updates position.
- handleButton(): Detects button presses and updates state.
- attachInterrupt(): Uses interrupts to detect rotary encoder and button events.
This code detects the rotary encoder’s direction and button presses, and writes this information to the serial monitor.