Scale From Zero to Millions of Users
Why Scaling is Necessary
When a website grows, its response time can slow down due to increased users. To prevent this, we need to scale our system.
Single Server Setup
Initially, everything (app, database, cache) runs on a single server.

Database
First step in scaling: move the database to a separate server.

Which Databases to Use?
- SQL: MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL
- NoSQL: CouchDB, Neo4j, Cassandra, HBase, Amazon DynamoDB
- NoSQL is good for super-low latency and massive amounts of unstructured data.
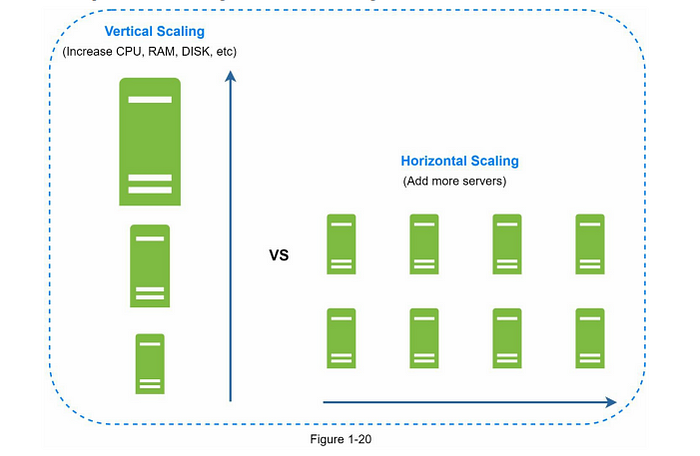
Vertical Scaling vs Horizontal Scaling
- Vertical Scaling: Add more power (CPU, RAM) to existing servers.
- Horizontal Scaling: Add more servers.
Load Balancer: Distributes incoming traffic among web servers.

Considerations for Load Balancer
- If server1 goes down, traffic is sent to server2.
- Add more servers as users increase.
Database Replication
Master/slave relationship where the master handles write operations, and slaves handle read operations.

Advantages
- Better performance.
- Reliability.
- High availability.
- Considerations
- Replace offline slave databases.
- Promote a slave to master if the master goes offline.
Cache
Stores frequently accessed data in memory to reduce database calls.

- Considerations
- Expiration Policy: Balance between too short and too long.
- Consistency: Sync cache data continually.
- Mitigating Failures: Use multiple cache servers.
- Eviction Policy: Least-recently-used (LRU) is common.
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Serves static content (CSS, JS, images, videos) from servers close to the user.

- Considerations
- Cost.
- Appropriate cache expiry.
- CDN fallback.

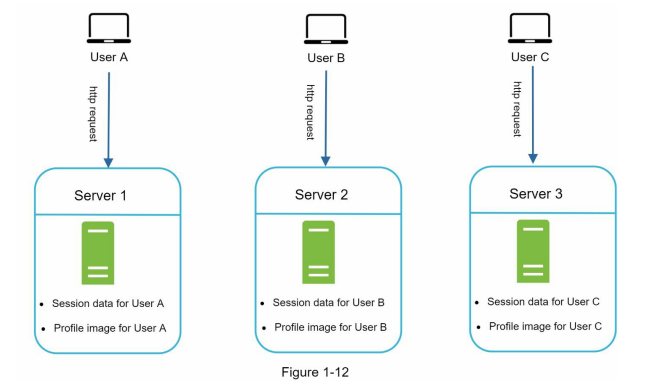
Stateful vs Stateless Architecture
- Stateful Server: Remembers client data between requests.
- Stateless Server: Keeps no state information.
Data Centers
Users are routed to the closest data center.
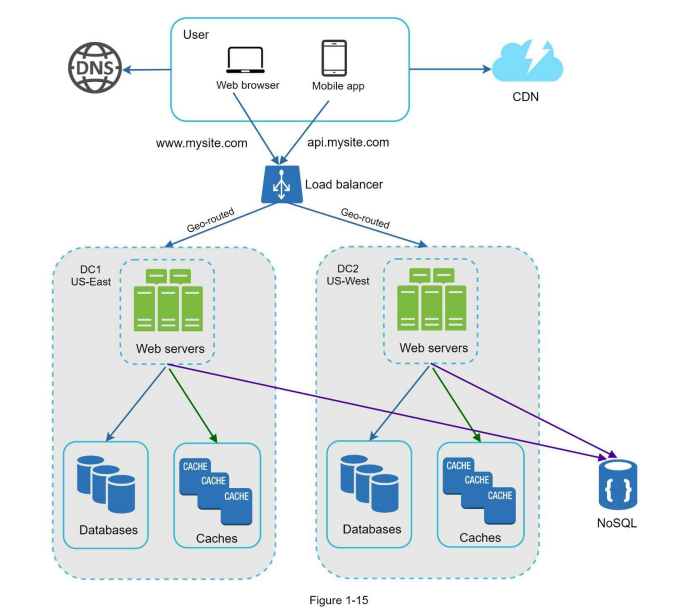
- Considerations
- Traffic redirection using geoDNS.
- Data synchronization.
- Test and deploy from different regions.
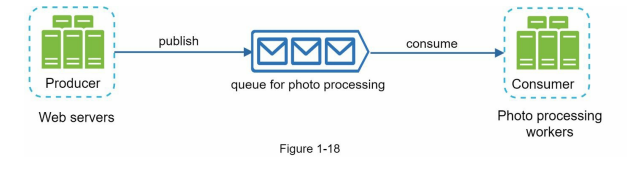
Message Queue
Supports asynchronous communication between services.
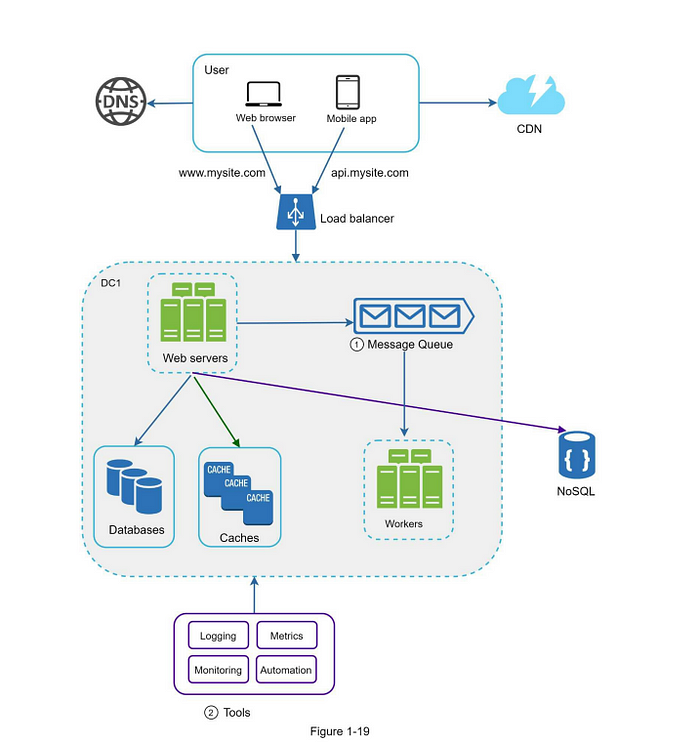
Logging, Metrics, Automation
- Logging: Monitor error logs.
- Metrics: Monitor CPU, memory, disk I/O, database, cache, daily active users.
- Automation: Use CI/CD tools to build, test, and deploy.
Scaling the Database
Vertical Scaling
Add more power (CPU, RAM, DISK) to an existing machine.
Horizontal Scaling (Sharding)
Separate large databases into smaller parts called shards.
- Considerations
- Reshard data if overloaded.
- Manage celebrity users separately.
- Hard to join and query across multiple shards.
Final System Illustration
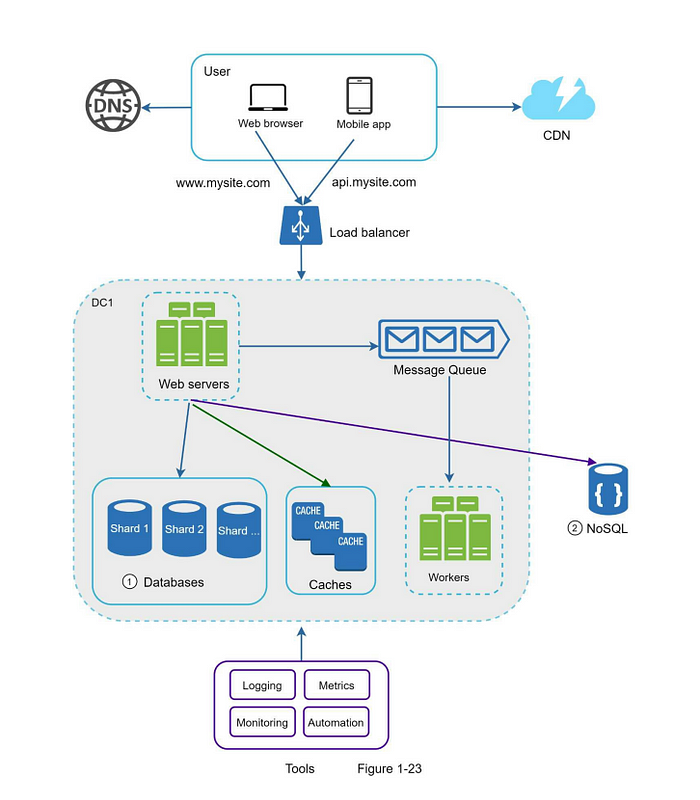
Millions of Users and Beyond
- Keep web tier stateless.
- Build redundancy at every tier.
- Cache data as much as possible.
- Support multiple data centers.
- Host static assets in CDN.
- Scale your data tier by sharding.
- Split tiers into individual services.
- Monitor your system and use automation tools.
Refs: