Most Essential JavaScript Functions and Usages
Finding the best JavaScript methods can be time-consuming due to outdated or multiple suggestions online. This article simplifies that process.
A comprehensive JavaScript function cookbook is being developed to help developers easily access essential functions and understand their usage. Bookmark these articles for quick reference!
The discussion ranges from basic to advanced functions, making it useful for beginner, intermediate, and pro JavaScript developers. Newly added JavaScript features are also explored.
Articles are segmented into sections:
- Strings
- Numbers
- Arrays
- Objects
- Dates
- Validations
- Plain Functions
Today’s focus is on Strings and Numbers.
Strings
String manipulation is fundamental in JavaScript. Understanding these functions is crucial.
01. Basics
Basic string manipulation functions:
const str = "Foods: Pizza, Bread";
// Splits the string into an array of substrings
str.split(" "); // [ 'Foods:', 'Pizza,', 'Bread' ]
str.split(":"); // [ 'Foods', ' Pizza, Bread' ]
// Returns a character at the specified index in a string
str.charAt(0); // F
str.charCodeAt(0); // 70 - Unicode decimal value of F
// Case conversion
str.toUpperCase(); // FOODS: PIZZA, BREAD
str.toLowerCase(); // foods: pizza, bread
// Replaces matches with a replacement
str.replace("Pizza", "HamBurger"); // Foods: HamBurger, Bread
// Extracts a part of the given string
str.substring(2, 5); // ods
str.slice(10); // za, Bread
str.slice(2, 5); // ods
str.slice(-5); // Bread
// Joins two or more strings
str.concat(", Rice"); // Foods: Pizza, Bread, Rice
// Finds the size of a string
str.length; // 19
// Removes whitespace from both ends
str.trim(); // Foods: Pizza, Bread
// Adds padding until it reaches the desired length
str.padStart(str.length + 5); // " Foods: Pizza, Bread"
str.padStart(20, "AB"); // "ABFoods: Pizza, Bread"
str.padEnd(20, "AB"); // "Foods: Pizza, BreadA"
For example, padStart and padEnd can mask a credit card number:
const cardNumber = "2012 4434 1121 2342";
const lastDigits = cardNumber.slice(-4);
const maskedNumber = lastDigits.padStart(cardNumber.length, "*");
console.log(maskedNumber); // ************2342
02. String Concatenation
Concatenate strings using concat, + operator, or template literals:
const str1 = "Hello";
const str2 = "World";
console.log(str1.concat(" ", str2));
console.log(str1 + " " + str2);
console.log(`${str1} ${str2}`);
concat()requires the invoking variable to be a string.+operator is simple and straightforward.- Template literals maintain readability with embedded expressions.
03. Converting to a String
Convert any type to a string:
const a = 225; // number
const b = true; // boolean
// Converting to string
const result1 = String(a);
const result2 = String(b);
console.log(result1); // "225"
console.log(result2); // "true"
Or use toString():
const bool = true;
const str = bool.toString();
console.log(str); // "true"
Differences:
value.toString()throws a Type Error ifvalueis null or undefined.String(value)does not.
04. Search
Several functions to search for a string:
const text = "Joe has a white car";
const position = text.indexOf("has");
console.log(position); // 4
const isInclude = text.includes("has");
console.log(isInclude); // true
const position2 = text.search("has");
console.log(position2); // 4
const result = sentence.match(exp);
console.log(result);
const matches = text.match(pattern);
console.log(matches);
const matchesAll = text.matchAll(pattern);
for (const match of matchesAll) {
console.log(match);
}
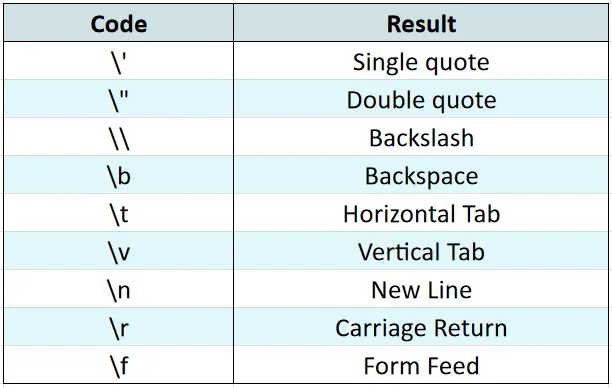
05. Escape Character
Manage special characters within strings using the escape character (\):
// Without escape characters
const message = "This is a "broken" string."; // Syntax error
// With escape characters
const message = "This is a \"fixed\" string."; // Correct
const name = 'His name is \'Peter\'.';
console.log(name); // His name is 'Peter'.
const nameTemplate = `His name is 'Peter'.`;
Numbers
01. String to Integer Number
Parse a string to an integer:
let num = Number.parseInt("34");
console.log(num); // 34
02. String to Float Number
Parse a string to a floating-point number:
let num = Number.parseFloat("34.235");
console.log(num); // 34.235
Rules for parsing:
- Stops at invalid characters.
- Returns
NaNif the argument’s first character can’t be converted.
03. Exponential Notation
Convert a number to its exponential form:
let num = 250000;
console.log(num.toExponential()); // 2.5e+5
console.log(num.toExponential(3)); // 2.500e+5
let num2 = 25005.45;
console.log(num2.toExponential(3)); // 2.501e+4
04. Handle Precision
Format a number to a specified length:
let num = 1255;
console.log(num.toPrecision(2)); // 1.3e+3
num = 13.3414;
console.log(num.toPrecision(3)); // 13.3
num = 13.3514;
console.log(num.toPrecision(3)); // 13.4
05. Language Sensitivity
Format numbers based on locale and formatting preferences:
let num = 762359.237;
// Indian
console.log(num.toLocaleString("en-IN")); // 7,62,359.237
// Chinese
console.log(num.toLocaleString("zh-Hans-CN-u-nu-hanidec")); // 七六二,三五九.二三七
// German
console.log(num.toLocaleString("de-DE")); // 762.359,237
// Japanese with options
const numberOptions = {
style: "decimal",
minimumFractionDigits: 2,
maximumFractionDigits: 2,
useGrouping: true,
};
console.log(num.toLocaleString("ja-JP", numberOptions)); // 762,359.24
// USD
console.log(
num.toLocaleString("en-US", {
style: "currency",
currency: "USD",
maximumSignificantDigits: 2,
})
); // $760,000
06. Boolean Checks
Validate numbers:
isInteger()isFinite()isNaN()
let num;
num = 45;
console.log(Number.isInteger(num)); // true
num = 386483265486;
console.log(Number.isFinite(num)); // true
num = NaN;
console.log(Number.isNaN(num)); // true
07. Rounding Off
Round numbers:
ceil()floor()round()
const num = 3.72;
const ceil = Math.ceil(num); // 4
const floor = Math.floor(num); // 3
const rounded = Math.round(num, 2); // 4
Round decimal places using toFixed():
let num = 250;
console.log(num.toFixed(2)); // 250.00
num = 25.5688;
console.log(num.toFixed(2)); // 25.57
num = 25.5648;
console.log(num.toFixed(2)); // 25.56
Tip of the Day
Measure function performance with time() and timeEnd():
console.time('timer-1');
let value = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
value += i;
}
console.timeEnd('timer-1'); // timer: 12.176ms
Explore more amazing methods on the MDN Web Docs.