Virtual POS Payment Models: 3D Secure, 3D Pay, 3D Host, Non Secure
TLDR: This guide explains the different virtual POS payment models—3D Secure, 3D Pay, 3D Host, and Non Secure—commonly offered by banks. It highlights the key differences in how these models handle transactions, focusing on identity verification, authorization, and customer experience.
In today’s financial environment, banks provide several payment methods. The article delves into the distinctions between these models for better understanding.
Key Terms:
- Gateway: Refers to the Virtual POS API.
- Provisioning: The process of transferring funds.
- Customer: Refers to the credit cardholder.
Popular payment models include:
- 3D Secure
- 3D Pay
- 3D Host
- Non Secure
While banks may use different terminology, the mechanisms remain consistent. For instance:
- 3D Secure may be referred to as 3D Model.
- 3D Host as 3D Hosting, 3D OOS, or 3D Secure Payment Page.
- Non Secure as Non 3D Secure, Standard Sale, or Non 3D Model.
When a merchant requests virtual POS services from a bank, they must specify the preferred payment model(s). Depending on their needs, one or more of these models can be activated.
Comparison
The diagrams below focus on specific steps that developers should handle while integrating virtual POS systems.
3D Secure Model
The most commonly used payment method, 3D Secure, involves a 3D password for identity verification before the provisioning process.
Workflow:
- Customer provides credit card details.
- A form is created using credit card, order, and virtual POS API account information.
- The form is posted to the bank’s URL, redirecting the customer to the bank’s site.
- After 3D verification, the customer is redirected back to the e-commerce site.
- If verification is successful, provisioning occurs.
Detailed diagram:
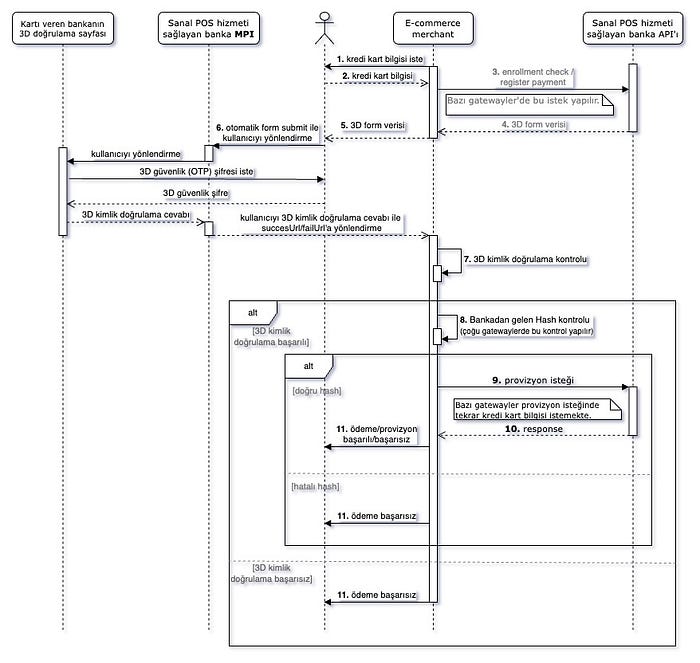
Key steps:
- Steps 3 and 4: These actions involve sending a request through a virtual POS gateway and processing responses. The response data is integrated into an HTML form.
- Step 5:
- Credit card, order, and response data are used to generate form values.
- A hash is generated using a secret key to authenticate the request.
- Hidden form fields are populated, and the form is submitted to the bank’s 3D gate URL.
- The form automatically submits using JavaScript, and the customer is redirected.
- The customer is redirected back to a success or failure URL, depending on the result.
<form method="POST" action="https://virtualpospaymentgatewaypre.akbank.com/securepay" name="redirect-form">
<input type="hidden" name="paymentModel" value="3D" />
<input type="hidden" name="okUrl" value="https://example.com/success.php" />
<input type="hidden" name="failUrl" value="https://example.com/fail.php" />
<!-- credit card and order data -->
</form>
<script>
setTimeout(function () {
document.forms['redirect-form'].submit();
}, 1000);
</script>
- Step 7: Depending on the gateway, the bank returns a response using POST or GET. Check the fields to verify the success of the transaction based on the
mdvalue.- md = 1: Verification successful.
- md = 2, 3, 4: Half-3D; the bank couldn’t fully verify the cardholder, but provisioning might still proceed.
- Other
mdvalues: Verification failed.
- Step 8: The bank’s response is hashed and compared with a calculated hash to ensure data authenticity.
- Step 9: Provisioning occurs, typically without credit card data. For some gateways, card data is required at this stage.
- Step 11: The customer is notified of the transaction’s success or failure.
3D Pay Model
3D Pay differs from 3D Secure in that the bank handles the provisioning process instead of the e-commerce site. The form data structure might vary slightly from the 3D Secure model.
Detailed diagram:
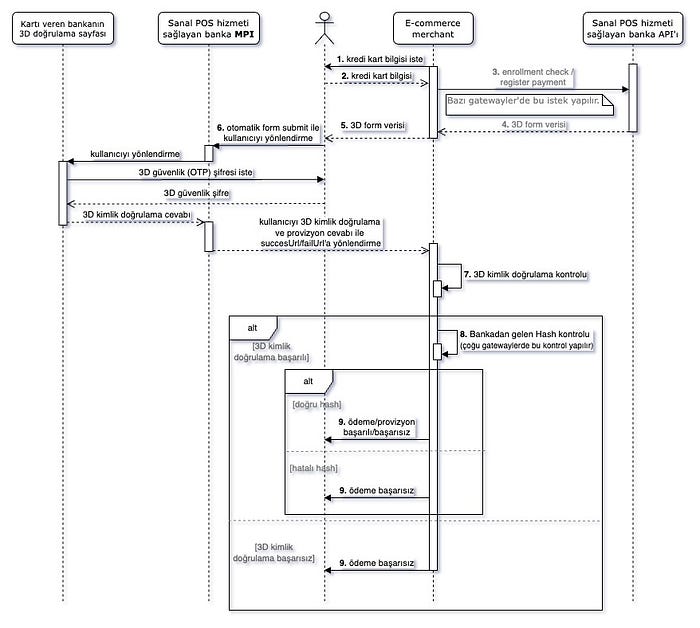
3D Host Model
In the 3D Host model, the customer’s credit card details are handled by the bank’s interface, and provisioning is also managed by the bank. Credit card information is not included in the form data.
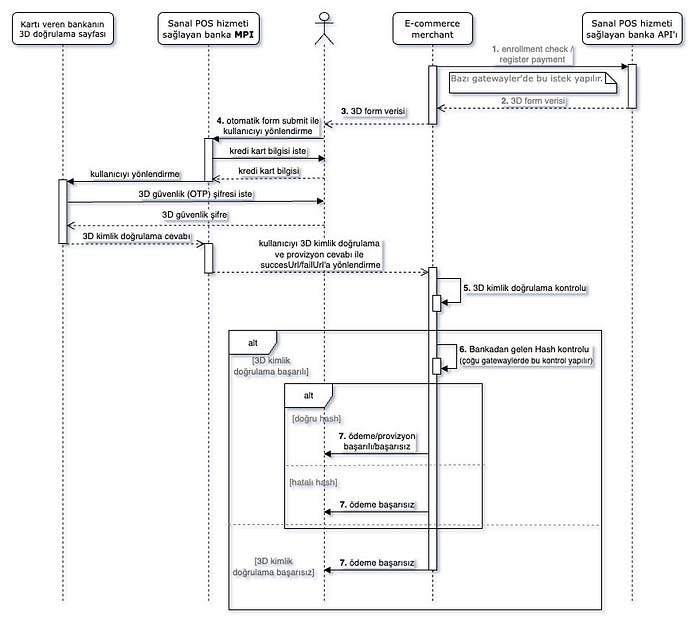
Non Secure Model
This method allows payments without 3D password authentication.
Workflow:
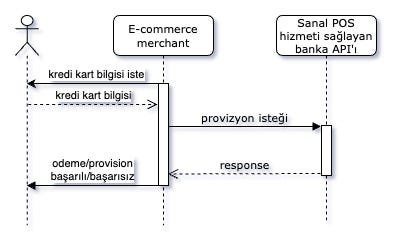
Virtual POS API Types
Some banks offer proprietary virtual POS systems, while others use third-party solutions like Payten. When switching from one bank’s Payten-supported POS to another, only the API credentials need updating, minimizing code changes.
Some banks provide multiple API options simultaneously. In some cases, banks offer third-party systems under their own branding.
Choosing the Right Payment Model
First, identify the payment models supported by the bank. Each gateway offers different models:
- For minimal development and 3D verification, choose 3D Host.
- The difference between 3D Pay and 3D Secure lies in the extra provisioning request, requiring more code for 3D Secure.
- Despite differences in naming, 3D Pay and 3D Host offer similar security to 3D Secure.
Why Use Non Secure Payments?
- Some platforms, like Hepsiburada, allow card storage for future transactions without 3D verification.
- Phone-based services may accept credit card info via phone for account recharging.
- Non Secure is necessary for pre-authorization closure, where blocked amounts are processed without cardholder presence, such as in car rentals.
Conclusion
While the workflows are consistent across gateways, the request structures can vary significantly:
- Some use XML, others use JSON.
- HASH algorithms and calculation methods differ.
- Data formats vary (e.g., 10 TL might be 10.0 or 1000).
Switching between gateways can be challenging due to these differences, despite having similar workflows.